A study from the Journal for Clinical Periodontology suggests that people with gum disease could have a higher chance of suffering complications related to COVID-19. This is due to the link between inflamed gums and the body’s inflammatory response.
Therefore, taking care of your gums is more important now than ever. You may feel tempted to skip routine appointments with your dentist. But your dentist provides crucial preventative dental care during these visits.
Gum disease is a common dental issue, but it could have severe consequences for your overall health if you do not get rid of it. Read on to learn more about gum disease’s effect on your oral health and why you should not ignore this problem.
Can I Tell If I Have Gum Disease?
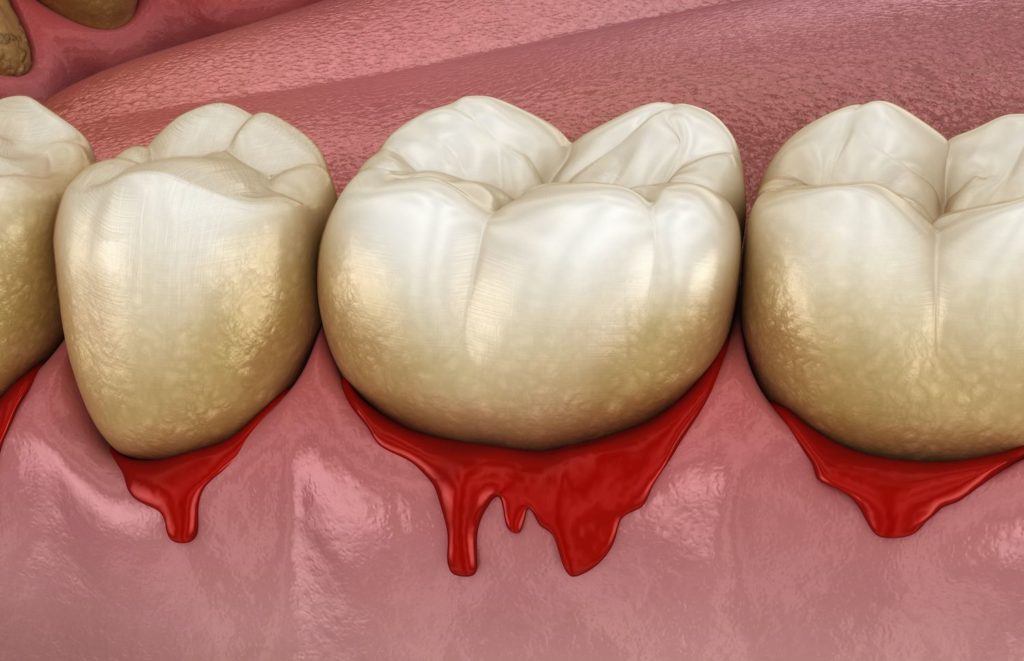
Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, can present with recognizable symptoms. These include puffiness, soreness, and bleeding in the gums. As the disease progresses, you might notice bad breath, looseness in the teeth, and gum recession.
Advanced gum disease or periodontitis can occur when the infection spreads from the gum tissue to deep within the tooth root and jawbone. While you might spot these symptoms, some cases of gum disease also have no visible symptoms at all.
This is why visiting your dentist for routine check-ups and periodontal screenings is so important. They can find signs of gum disease and offer prompt treatment before the infection spreads. If the disease progresses, the issue grows harder to treat and may leave you with irreversible dental damage like tooth loss.
Can I Treat Gum Disease on My Own?
Once you contract gum disease, you cannot get rid of it on your own. You will need intervention from your dentist to eradicate this disease.
If your dentist diagnoses you with gum disease, they can begin treating you right away. They will begin with a thorough teeth cleaning to get rid of plaque and tartar build-up along with excess bacteria. They can clean deep in the gum pocket with a technique known as scaling and root planing.
The dentist may also suggest using antibacterial mouthwash or toothpaste at home. These items can balance the natural bacteria in your mouth, lowering the risk of their spread across your teeth and infecting the gum tissue. This will prevent gum disease from returning as well as decrease uncomfortable symptoms.
If gum disease persists after this treatment, you may need more extensive periodontal therapy. This may involve a referral to a specialist who can target the damaged gum tissue to get rid of the infection. You might need a minimally invasive procedure or oral surgery, depending on your unique dental needs.
Though you cannot treat gum disease on your own, you can take efforts to prevent it. You can lower your risk of this infection by practicing good oral hygiene. This involves flossing each day and brushing your teeth twice per day. For more information on how we diagnose and treat gum disease, please visit Periodontal disease treatment. Ask Your Dentist for more periodontal health tips.
